Understanding Selection Sort in Computer Science: A Comprehensive Overview
0 comments
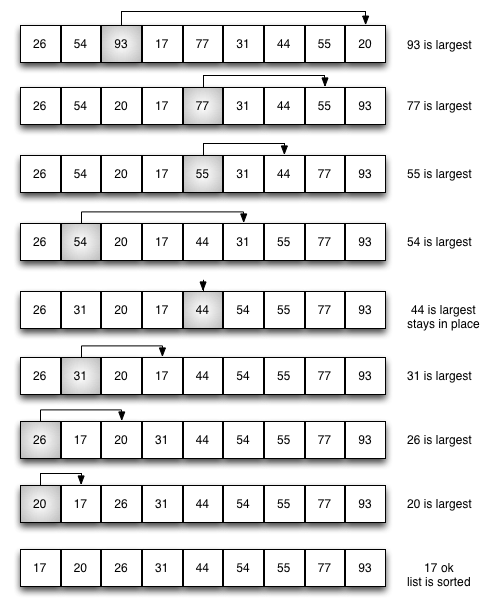
In the vast landscape of sorting algorithms, Selection Sort is a fundamental and straightforward technique computer scientists use to arrange elements in ascending or descending order. As a computer science student, delving into the intricacies of sorting algorithms is crucial for building a solid foundation in algorithmic design and analysis. This essay explores the essence of Selection Sort, its working principles, time complexity, advantages, and limitations, shedding light on its significance in computer science.
Selection Sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that divides the input list into two parts: a sorted and an unsorted region. The algorithm repeatedly selects the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted area and swaps it with the first unsorted element. This process continues until the entire list is sorted.
The core idea behind Selection Sort is its simplicity. Unlike more complex algorithms such as Merge Sort or Quick Sort, Selection Sort's uncomplicated nature makes it an excellent choice for small datasets or as an educational tool for understanding sorting fundamentals.
The step-by-step procedure of Selection Sort can be briefly described as follows:
Initialization - The algorithm considers the entire list unsorted.
Iterative Selection - Selection Sort identifies each iteration's minimum (or maximum) element in the unsorted region.
Swap - The identified minimum (or maximum) element is then swapped with the first element in the unsorted region.
Partitioning - One element expands the sorted region, and one element reduces the unsorted area.
Repeat - Steps 2-4 are repeated until the entire list is sorted.
Analyzing the time complexity of an algorithm is crucial for evaluating its efficiency significantly as the input size increases. In the case of Selection Sort, the time complexity is O(n^2), where 'n' represents the number of elements in the list.
This quadratic time complexity arises from the nested iteration structure of the Selection Sort. In the worst-case scenario, the algorithm must traverse the remaining area for each element in the unsorted region to find the minimum (or maximum) element. Consequently, the overall time complexity becomes proportional to the square of the input size.
Simplicity - One of the primary advantages of Selection Sort is its simplicity. The algorithm's straightforward implementation makes it easy to understand, making it an excellent introductory sorting algorithm for students.
In-place Sorting - Selection Sort performs in-place sorting, meaning it does not require additional memory space to store intermediate results. This is advantageous in situations where memory is a critical resource.
Minimization of Swaps - Unlike other sorting algorithms, Selection Sort minimizes the number of swaps required to arrange elements in order. Since swaps are typically more time-consuming than comparisons, this can be advantageous in specific scenarios.
Quadratic Time Complexity - The most significant limitation of Selection Sort is its quadratic time complexity. As the input size increases, the algorithm's efficiency decreases rapidly, making it impractical for sorting large datasets.
Lack of Adaptability - Selection Sort's performance remains the same, regardless of the initial order of elements. This lack of adaptability makes it less suitable for partially sorted or nearly sorted lists, where more efficient algorithms like Insertion Sort may be more appropriate.
Unstable Sorting - Selection Sort is an unstable sorting algorithm, meaning it does not guarantee to preserve the relative order of equal elements. If two equal elements exist in the unsorted region, the algorithm may swap them, potentially altering their original order.
While Selection Sort may not be the most efficient sorting algorithm in practical scenarios, its significance in computer science education cannot be overstated. It serves as a fundamental building block for students to grasp essential algorithmic design and analysis concepts. Through the implementation and analysis of Selection Sort, students can develop a solid understanding of sorting algorithms, time complexity, and the trade-offs inherent in algorithm design.
Moreover, the simplicity of Selection Sort allows students to focus on the core principles of sorting without getting bogged down by intricate details. This algorithmic clarity facilitates the transition to more complex sorting algorithms and lays the groundwork for tackling broader challenges in algorithmic problem-solving.
In conclusion, Selection Sort stands as a cornerstone in sorting algorithms, offering a simple yet insightful introduction to the principles of algorithmic design. As a computer science student, a comprehensive understanding of Selection sorting provides the foundation for delving into more advanced sorting techniques and broader algorithmic concepts. While its practical use may be limited in comparison to more efficient algorithms, the educational value of Selection Sort in fostering algorithmic intuition and analytical skills cannot be understated. Computer science students can glean valuable insights that will undoubtedly contribute to their growth and proficiency in the field by exploring its working principles, time complexity, advantages, and limitations.
Posted using



Comments